17°C
The Morosini fountain, also known to the citizens of Heraklion as Liontaria (= lions) is one of the most remarkable monuments of the city.
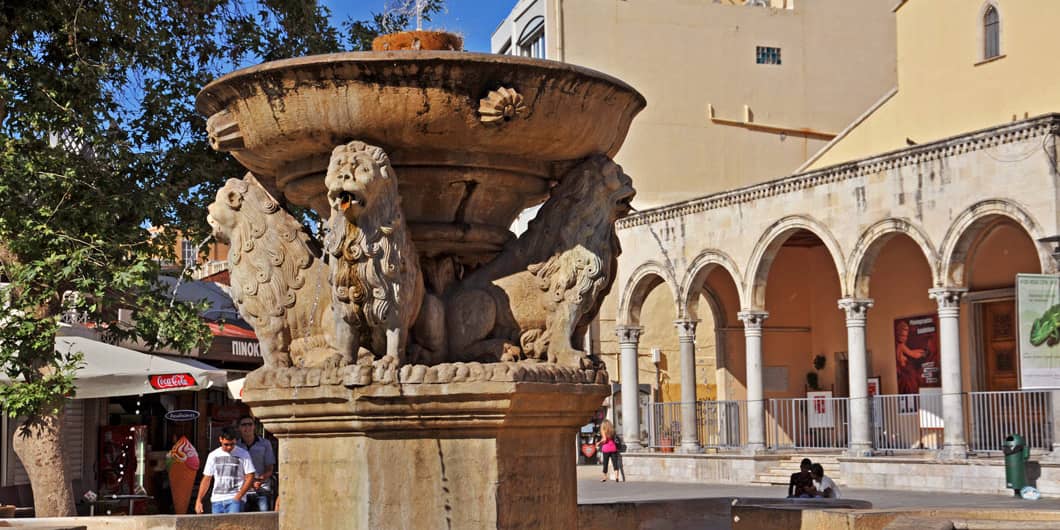

It is an impressive sculptural composition, the erection of which was ordered in 1628 by Francesco Morosini, governor of Crete, thus the fountain was named after him.
Morosini actually created a whole aqueduct system that channelled the spring water of the Archanes area to the city of Heraklion, of which the Morosini fountain was the last part.
A large carved marble basin collects the water which springs from a spout on top of the Morosini fountain. This basin is supported by four marble lions, and it also used to have a marble statue of the god Poseidon holding a trident, which was unfortunately destroyed in the years of Turkish occupation. The sculpted reliefs on the basin represent themes from the Greek Mythology.
Architecture
Open-Well maintained
Venetian Period
Lions Square
For the Rural Greece accessibility is fundamental to enhancing an inclusive tourism experience. Following the principles of inclusion and equality, the epaithros Rural Tourism Network and its member businesses are constantly working to enhance the tourism services provided, ensuring that all visitors have the opportunity to experience the authentic beauty of the Greek countryside.
Sustainability in tourism refers to a way of developing tourism that respects and protects the environment while strengthening the local economy and preserving cultural traditions. The aim of sustainable tourism is to provide unique and authentic experiences for visitors without harming the natural and social environment, while ensuring that local communities benefit from tourism activity.
This type of tourism is based on three pillars:
With sustainable tourism, visitors can have authentic experiences, knowing that the impact of tourism on the region is positive and lasting for future generations.
For Rural Greece, localism is one of the most important factors for the development of sustainable tourism, as it promotes a strong link between the tourism product and the local society, economy and culture. Through localism, visitors get the opportunity to explore authentic elements of the destination, such as local products, traditions and culture. This not only boosts the local economy, but also helps to sustain and strengthen local businesses, creating new jobs and supporting the development of local communities.
Furthermore, localism contributes to the sustainability of the tourism sector, as it reduces the use of resources from other regions and encourages the use of local goods and services, reducing the ecological footprint of tourism activities. Thus, integrating localism into tourism practices enhances sustainability awareness, both among visitors and local businesses, creating a more responsible and sustainable tourism destination.